
EPICC molecules are derived from a human enteric virus that has adapted over 1 billion years of evolution. The viral capsids are composed of a simple structure of 180 copies of a single protein consisting of 787 amino acids. This virus does not generate immune responses and possesses a unique dual targeting mechanism inhibiting humoral and cellular inflammation.
Peptides derived from this capsid protein maintain both the humoral and cellular immune inhibition activity of the virus. The EPICC technology is built on a library of more than 150 of these dual action peptides.
Therapies derived from viruses have been a source of Nobel prize winning scientific advancements and discoveries. Many drugs currently on the market are derived from natural sources, such as antibiotics.

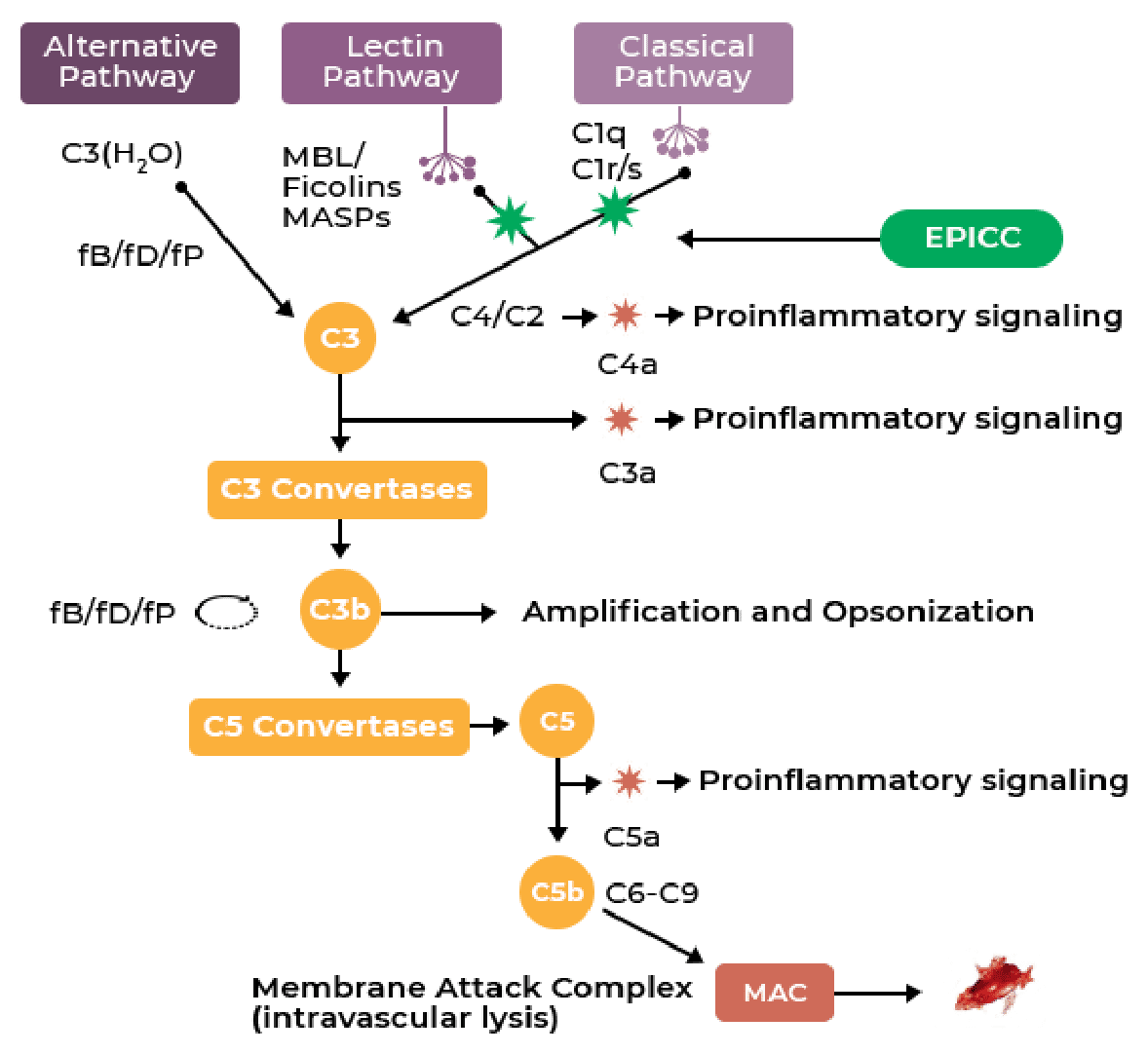
The EPICC platform presents a novel opportunity to modify disease progression through moderation of the most robust components of both humoral (complement system) and cellular (neutrophils) components of innate immunity.
EPICC molecules rapidly and dose dependently inhibit C1 and MBL, the earliest initiators of the classical and lectin complement pathway. Inhibition is via transformational changes of serine proteases at C1 and MBL.
Selective upstream targeting of the complement system increases selectivity, efficacy, and reduces adverse events.
EPICC molecules do not interfere with C1q homeostatic functions and preserve the alternative pathway, maintaining the body’s immunosurveillance capacity.
EPICC molecules’ small size and function lead to excellent tissue penetration.
In addition to complement modulation, the EPICC platform acts as a potent inhibitor of innate, neutrophil-mediated, inflammatory processes, including inhibition of MPO activity and NETosis.
Blocks MPO activity which generates hypochlorous acid and host tissue injury.
Inhibits NETosis, a neutrophil death pathway contributing to host tissue damage.
Exhibits anti-oxidative properties and neutralizes free radicals in the body.
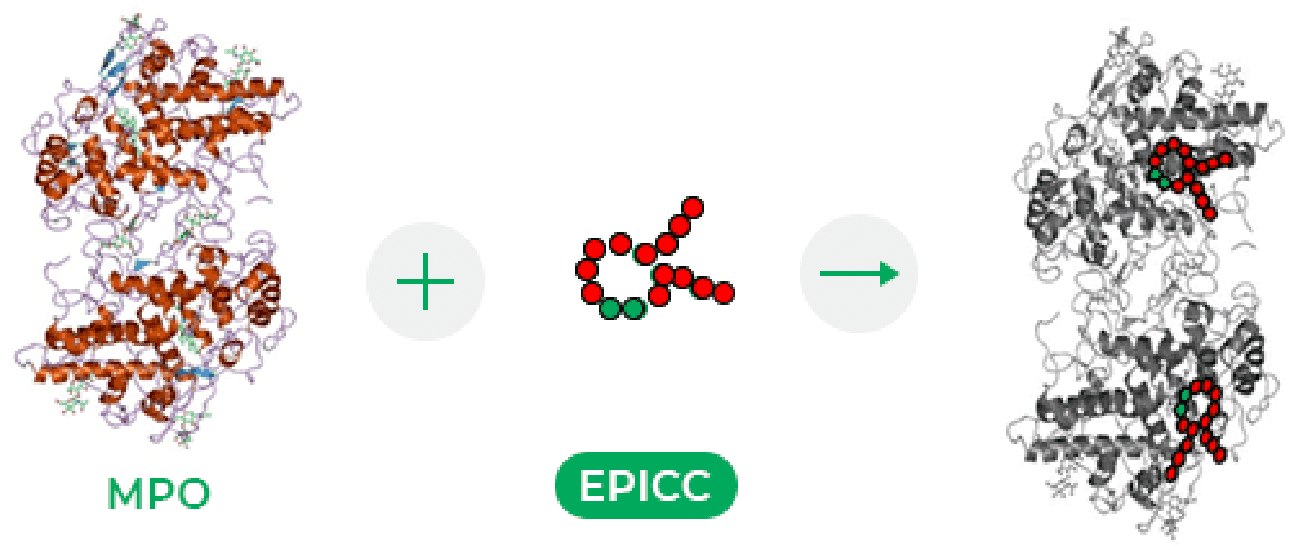
MPO catalyzes formation of hypochlorous acid and tyrosyl radicals, and is released by neutrophils and innate immune cells, contributing to inflammation.

EPICC molecules’ cysteine-rich region modulates the peroxidase activity of MPO, blocking hypochlorous acid formation and preventing neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation.
Our lead compound RLS-0071 has an excellent safety profile to date, with two healthy adult studies completed including over 60 subjects dosed and over 500 doses administered. Side effect profiles were similar to placebo subjects. Safety data can be shared under confidentiality.
RLS-0071 has had widespread scientific review and support. Scientists conducting research on RLS-0071 capabilities have published 25 peer-reviewed and indexed studies. A number of leading research organizations, including the NIH, National Multiple Sclerosis Foundation, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, VA Catalyst and the Commonwealth Transfusion Foundation have provided grant funding to ReAlta.